Commvault Unveils Clumio Backtrack - Near Instant Dataset Recovery in S3
How to Create a Reliable Amazon S3 Backup Strategy
Backing up data is essential to data resilience and cybersecurity. Having a comprehensive S3 backup strategy can help ensure that your data is secure and easily retrievable in the event of a data loss or system failure. This article will provide an overview of the basics of S3 backup, as well as best practices for creating and implementing a secure and reliable S3 backup strategy.
Understanding the Basics of S3 Backup
S3 is Amazon Web Services’ cloud-based object storage service. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers, and is ideal for storing and retrieving large amounts of data. S3 has become extremely popular for storing unstructured data due to its low cost and scalability. When using Amazon S3 for data storage, it is essential to be aware of the shared responsibility model, which holds customers accountable for their data validity, security, accessibility, and usability.
AWS will not be liable to restore the customer’s data if it gets deleted, corrupted, or ransomed. As per Gartner’s research, 95 percent of cloud security failings by 2022 will be the customer’s fault; thus customers should make sure their Amazon S3 data is protected and backed up.
Creating a backup of S3 is a key component of any cloud data protection strategy. This is because of the various scenarios where data loss can occur, such as software overwrites, malicious attacks enabled by weak credentials, ransomware, insider threats, and accidental deletions during life-cycling and migration.
In addition to ensuring recovery in the event of a data loss, backing up S3 also helps safeguard against future threats or operational disruptions. By making Amazon S3 backup part of an organization’s data protection plan, they can reduce the impact of data loss and ensure a successful recovery.
Developing a Secure S3 Backup Plan
The first step in creating a secure S3 backup strategy is to determine what subset of data needs to be backed up and how often. Additionally, you should consider the method of your S3 backups and its associated cost. It is also important to consider the security of your data when creating a backup plan.
Next, you should ensure that your data is encrypted and that access to the data is restricted to authorized users. Finally, you should regularly review your backup plan to ensure that it is up to date and that it meets your security requirements.
When dealing with large amounts of data on S3, it is essential to have the ability to selectively backup and restore specific data, in order to save on costs and time to recover. You should choose a solution that allows you to protect and retrieve large S3 buckets or data lakes selectively—at the level of files, objects, or prefixes.
The majority of data in an S3 data lake, for example, may require only 30 days of retention for operational recoveries. But it may also contain compliance-subject sensitive information that needs to be retained for several years.
The S3 backup strategy also needs to account for flexible backup frequency (continuous, daily, weekly, monthly etc.), as well as specific point in time recovery. This can be vital in case of data corruption or accidental deletions, allowing you to return the exact data you need to the last known good state.
Understanding AWS tools for securing S3 data
Amazon S3 provides several ways to version and create copies of data, including Object Versioning, S3 Replication, and AWS Backup for S3. Each method has its own advantages and drawbacks. Object Versioning keeps a version of every change made to each object in a bucket for a specified period of time. This is an excellent strategy for operational recoveries. However, this can turn out to be extremely expensive for large or fast-changing buckets, since each object change is tracked, whether required or not.
S3 Replication copies data from one source to another and is a great tool for increased resilience and availability, but because it requires versioning to be enabled, it carries the same drawbacks. As with versioning, replication does not offer point in time recovery, does not protect against ransomware, and cannot be construed as a backup solution.
AWS Backup for S3 protects many different AWS services, including S3, and offers a rich feature set including point in time recovery. However, AWS Backup maxes out at a scale of 3 billion objects per bucket, does not offer the granularity to protect and objects individual prefixes (only offers all-or-nothing bucket-level backup), and requires S3 versioning to be enabled.
Finally, AWS Backup does not support cold storage and cross-account grouping of objects and prefixes into common policy or compliance-oriented pools.
Some users deploy a periodic copy-and-archive method as a proxy for backup tools—this is a risky strategy since versions and changes may not be tracked correctly, the solution is not air gapped, it can get very expensive to maintain, and it is likely exceedingly difficult to find the right copy to restore for consistency.
Keep an eye out for the following cost pitfalls when it comes to backing up S3 data:
- Backing up all data, even if it is not critical
- Using costly tools meant for disaster recovery and replication as proxies for backup solutions
- Storage spend, especially when it comes to small files that are metered at 128 kB
- Buckets or objects that are incorrectly locked against deletions for long periods
- Additional copies in vaults for air gap and compliance requirements, which incurs continuous and recurring charges over the lifetime of the data
Establishing Access Control to Your S3 Backups
Once you have determined the type of data that needs to be backed up, the next step is to establish access control to your S3 backups. You should use identity and access management (IAM) roles to control who can access your S3 backups. Ensure that your policies are updated regularly to reflect any changes in engineering personnel responsible for backups.
As with your primary data, best practice is to use Multi-factor authentication to secure your backup solution. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your S3 backups are secure and that only authorized users can access them.
Utilizing an air gap backup solution like Clumio offers an additional layer of protection against malware or ransomware, as backup data is isolated and stored on a different security domain than the main system. Customers are ensured of secure storage since the resident data cannot be changed or deleted. They no longer need a third copy of their data stored on a separate air-gapped location, since Clumio is air-gapped by design.
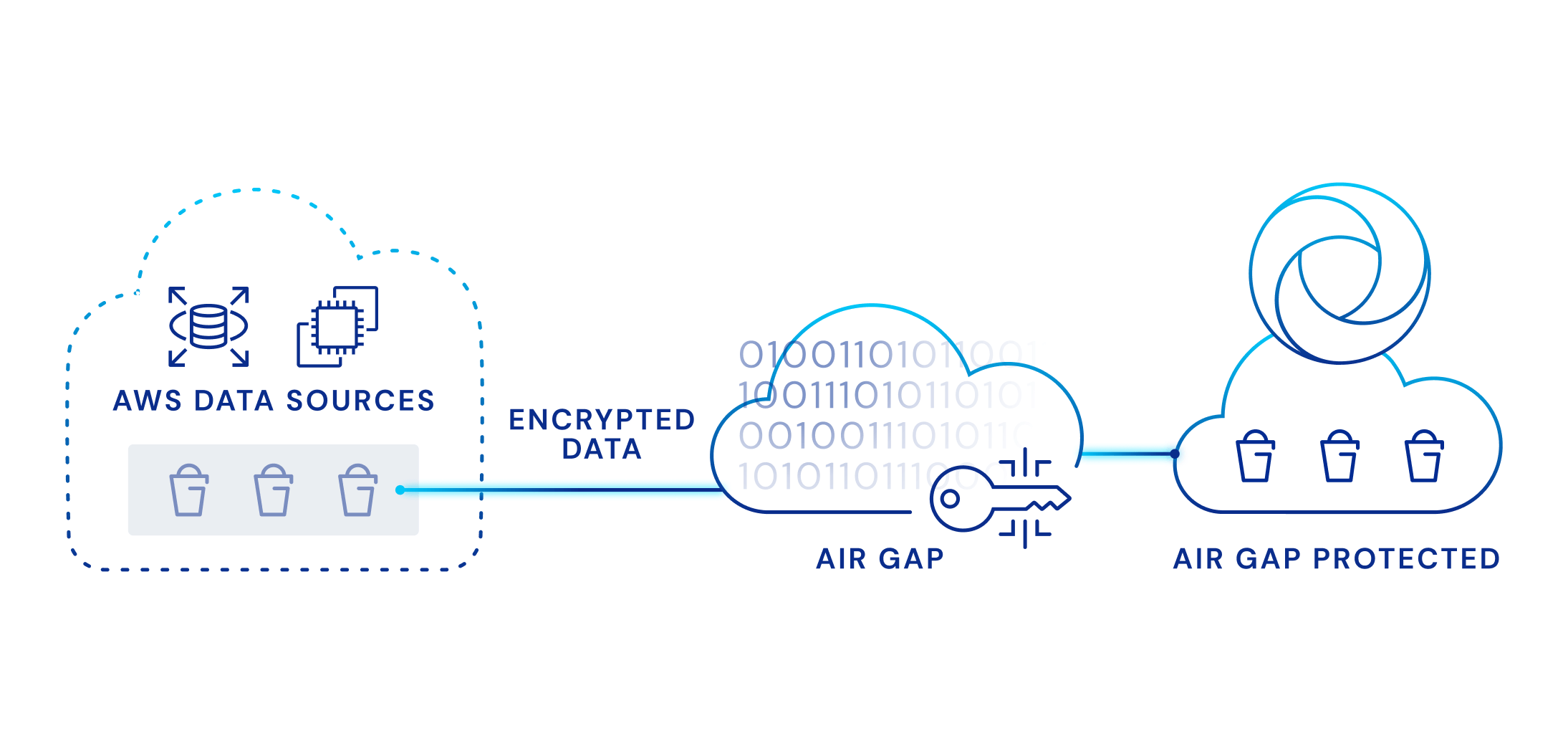
Setting Up Encryption for Your S3 Backups
Encryption is an important part of any secure S3 backup strategy. Encryption helps to protect your backed up data from unauthorized access. To do this, you should use an encryption key that is generated and stored securely within your organization, preferably in conjunction with Amazon’s key management system (KMS). Additionally, you should regularly rotate the encryption key to ensure that your data remains secure.
Implementing Monitoring and Auditing of Your S3 Backups
To ensure that your S3 backups are secure and compliant, it is important to monitor and audit them regularly. You should audit log files on a regular basis to ensure that your backups are being created correctly and no unauthorized access to your data has occurred.
Look to automated tools like proactive warnings to alert you if backups fail or other issues are identified. This can help you quickly identify any issues with your backups and take corrective action.
Automating the Process of Backing Up S3 data
Once you have established the method, access control, and encryption for your S3 backups, the next step is to automate it. When automating the process of backing up to S3, it is important to consider the frequency of backups, the duration for which they should be retained, and the class of storage they should be backed up to.
Testing Your S3 Backup Strategy
You should test your backups by performing controlled restores regularly to ensure that they will be successful when needed. You can do this by restoring data from a backup and verifying its accuracy. The restore process should be tested periodically to ensure that it is working properly and meeting your business goals and service level agreements (SLAs).
Troubleshooting Common Issues with S3 Backup Strategies
If you encounter issues with your S3 backups, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot them. First, check the logs associated with your backups to see if there are any errors or warnings that may indicate an issue. Additionally, check the IAM roles and policies associated with your backups to ensure that they are properly configured. Some backup services offer automated proactive customer support which will detect a failed backup or restore and reach out to alert you.
Summary: Best Practices for Securing Your Business Data with an S3 Backup Strategy
S3 data is becoming increasingly critical, and it is now crucial to back up this data and keep it secure. To achieve this—
- Select which data in your S3 buckets or data lakes to back up
- Establish the right method
- Define access control policies and air gaps
- Make sure they’re encrypted and immutable
- Monitor and audit your backups regularly
- Automate the backup process using predefined policies
- Test your backups periodically
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your data is safe and easily retrievable in the event of a data loss or system failure. Want expert guidance in designing your strategy? Contact us for advice.
